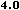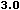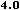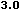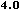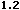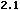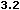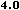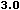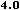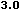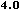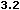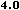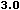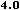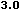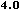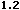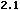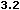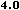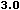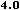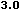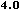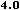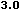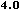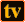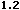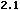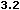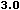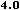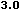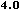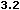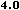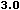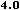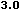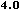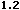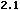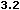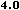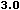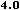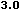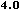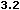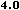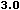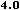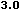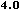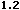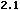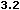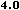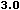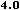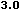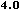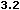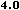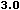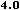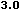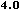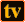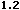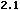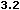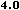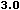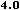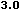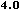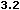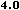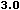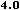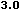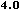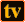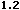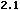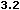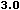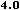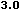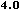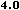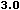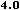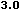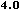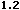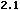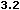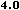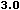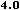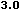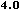<A>...</A>
Description
This element is what the hyperlinked structure of the World Wide Web is based
on. It is used in two ways:
- 1. Create a hyperlink to another anchor
- By using the HREF attribute you create an hyperlink, this is a link which
points to another document, somewhere on the internet. When a user selects
this link, the browser will load the resource that the link refers to.
- 2. Create an anchor in a document
- When you use the NAME or ID attribute you create an anchor, this is a
position inside a document which can be used as the target for an
hyperlink.
DTD
<!ELEMENT A - - (%inline;)* -(A) -- anchor -->
<!ATTLIST A
%attrs; -- %coreattrs, %i18n, %events --
charset %Charset; #IMPLIED -- char encoding of linked resource --
type %ContentType; #IMPLIED -- advisory content type --
name CDATA #IMPLIED -- named link end --
href %URI; #IMPLIED -- URI for linked resource --
hreflang %LanguageCode; #IMPLIED -- language code --
rel %LinkTypes; #IMPLIED -- forward link types --
rev %LinkTypes; #IMPLIED -- reverse link types --
accesskey %Character; #IMPLIED -- accessibility key character --
shape %Shape; rect -- for use with client-side image maps --
coords %Coords; #IMPLIED -- for use with client-side image maps --
tabindex NUMBER #IMPLIED -- position in tabbing order --
onfocus %Script; #IMPLIED -- the element got the focus --
onblur %Script; #IMPLIED -- the element lost the focus --
>
from the
HTML 4.0 DTD,
"Copyright ©
W3C,
(MIT,
INRIA,
Keio).
All Rights Reserved."
Attributes
Core attributes:
class
id
style
title
Internationalization attributes:
dir
lang
Events:
onclick
ondblclick
onmousedown
onmouseup
onmouseover
onmousemove
onmouseout
onkeypress
onkeydown
onkeyup
ACCESSKEY
Description of the accesskey
attribute
CHARSET
This attribute specifies the character encoding of the resource to which the
link points.
HREF
Create a link to an URI, a Universal Resource Identifier (see
RFC 1630
 for the complete RFC).
for the complete RFC).
A URI consists of the following elements :
<protocol>://<host>:<portnumber><path><anchor>?<parameters>
- protocol
- The protocol you want to use. Some well-known protocols are :
| Protocol |
Usage |
| http |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol, for World Wide Web pages
|
| ftp |
File Transfer Protocol, for downloading and uploading files
|
| news |
Reading and posting messages to newsgroups
|
| gopher |
Menu like information system, used before the WWW got popular.
|
| telnet |
Remote login on another computer
|
| javascript |
Trigger the execution of a JavaScript function
|
- host
- The host computer which has to handle the request. This can be a
four-number internet address, or the name of the computer.
- portnumber
- On a computer you can set up more than one server (program) which handle
the same protocol. Each server is assigned its own portnumber to which it
listens. Each protocol has a default portnumber, and most programs add
this if the address does not contain a portnumber. For example the default
portnumber for http is 80.
- path
- The directory on the computer where the information is stored.
- anchor
- For an HTTP address you can create anchors in a page, which lets you jump
to a specific position in that page. Anchors are created with the NAME
attribute of the A element.
- parameters
- If the address links to a program you can supply information to this
program with this parameters. What parameters you can use depends
completely on the program.
If you want to link to an anchor which has been created with the NAME attribute,
Add the character # followed by the name of the anchor to the link. By using
only the #<NAME> syntax as the destination of the link you can link to a
specific position with the current document. This can be used for things like a
table of contents.
HREFLANG
This attribute specifies the base language of the resource where this link
points to. The HREF attribute must be supplied when this attribute is present.
NAME
Give the anchor a name that can be used as the target of an URL in the HREF
attribute. This makes it possible to jump to a specific place in the target
document. To use this position add the character #, followed by the name to the
URL in the link. The attribute ID can be used for the same purpose.
The value supplied is case-sensitive, and must be unique within a document.
Although case-sensitive, two values which only differ in case
are not allowed.
NOCOLOR
This prohibits the text of the link to be drawn using the color which was set
with the LINK attribute of the BODY element.
ONBLUR
Description of the ONBLUR attribute
ONFOCUS
Description of the ONFOCUS attribute
REL
This attribute defines the relation between the current document and the anchor
to which the link points. The value is called the "link type". The
value for this attribute is a list of link types separated by spaces.
Known link types are:
- Alternate
- Designates substitute versions for the document in which the link occurs.
When used together with the lang attribute, it implies a translated
version of the document. When used together with the media attribute, it
implies a version designed for a different medium (or media).
- Stylesheet
- Refers to an external style sheet. This is used together with the link
type "Alternate" for user-selectable alternate style sheets.
- Start
- Refers to the first document in a collection of documents. This link type
tells search engines which document is considered by the author to be the
starting point of the collection.
- Next
- Refers to the next document in an linear sequence of documents. User
agents may choose to preload the "next" document, to reduce the perceived
load time.
This is the only value supported by WebTV.
- Prev
- Refers to the previous document in an ordered series of documents. Some
user agents also support the synonym "Previous".
- Contents
- Refers to a document serving as a table of contents. Some user agents also
support the synonym ToC (from "Table of Contents").
- Index
- Refers to a document providing an index for the current document.
- Glossary
- Refers to a document providing a glossary of terms that pertain to the
current document.
- Copyright
- Refers to a copyright statement for the current document.
- Chapter
- Refers to a document serving as a chapter in a collection of documents.
- Section
- Refers to a document serving as a section in a collection of documents.
- Subsection
- Refers to a document serving as a subsection in a collection of documents.
- Appendix
- Refers to a document serving as an appendix in a collection of documents.
- Help
- Refers to a document offering help (more information, links to other
sources information, etc.)
- Bookmark
- Refers to a bookmark. A bookmark is a link to a key entry point within an
extended document. The title attribute may be used, for example, to label
the bookmark. Note that several bookmarks may be defined in each document.
REV
This attribute defines the relation between this anchor and another document
that points to this anchor. It is the reverse of the REL attribute. The value
is called the "link type" and is a list of link types separated by
spaces.
See the REL attribute for the possible values for this attribute.
SELECTED
Use the selected attribute to indicate that this anchor should be initially
selected with the yellow Highlight rectangle. If two anchors in one web page
have the selected attribute, the first one in the HTML definition will be
selected. This corresponds to the anchor closest to the top-left of the page.
The selected anchor may not appear in the first screenfull of the page. The
WebTV interface won't scroll to that anchor in order to make it appear.
Instead, the selection will appear when the viewer scrolls to that part of the
page.
TABINDEX
Description of the TABINDEX attribute
TARGET
The TARGET attribute forces the load of that link into a targeted window. It
is only used in combination with the HREF attribute.
The value supplied with the attribute must be the same as the name of the
window, and is case-sensitive. You can give a window a name with the
FRAME element. If a window with the supplied
target name does not exist then a new window will be created with that
name.
If you do not specify a target window the current window will be used, or the
target specified with the BASE element.
These names all begin with the underscore character. Any targeted window name
beginning with underscore which is not one of these names, will be ignored.
| Value |
Description |
| _blank |
This target will cause the link to always be loaded in a new blank window.
This window is not named.
|
| _self |
This target causes the link to always load in the same window the anchor was
clicked in. This is useful for overriding a globally assigned BASE target.
|
| _parent |
This target makes the link load in the immediate FRAMESET parent of this
document. This defaults to acting like _self if the document
has no parent.
|
| _top |
This target makes the link load in the full body of the window. This
defaults to acting like _self if the document is already at the
top. It is useful for breaking out of an arbitrarily deep FRAME nesting.
|
TYPE
This attribute specifies the content-type of the resource to which this link
points. The value of this attribute must be a MIME type. A MIME type defines
what kind of resource the link points to. For example, a HTML file has a MIME
type of text/html.
Examples
 |
Here's a link to
<A href="#top" onclick="alert('Go! link Go!')">the top of the page</A>.
|
| |
 |
|
Here's a link to
the top of the page.
|
| |
 |
A link to a zip file : <A href="htl.zip">download this list</A>
|
| |
 |
|
A link to a zip file : download this list
|
| |
 |
Create a link to <A href="mailto:schluter@knoware.nl">my email address</A>
|
| |
 |
|
Create a link to my email address
|